Connected CMMS
Preventive Maintenance Inspections Guide: How to Prepare, Execute, and Sustain Optimal Equipment Performance
So, you've finally decided to implement preventive maintenance inspections for your facility. You've built out your maintenance team. You have a few expectations in place.
And now, you find yourself with a whole new set of problems.
Suddenly, planning inspections isn't enough. Everyone’s looking at the ROI of your maintenance activities.
Have you covered every critical component? Did you consider all potential points of failure in your maintenance strategy? Is your approach comprehensive, leaving no room for oversight?
In short, how effective are your maintenance inspections?
In this guide, we'll provide you with concrete, actionable tips to enhance your preventive maintenance inspection efficiency without compromising effectiveness, allowing you to implement them today.
What are Preventive Maintenance Inspections?
The overall goal of preventive maintenance inspection is to:
- Identify and address potential issues before they turn into costly problems.
- Prolong the lifespan of equipment and assets through regular care and attention.
- Minimize unplanned downtime and maintain a smooth and efficient operation.
- Enhance safety by ensuring that equipment is in optimal working condition, reducing the risk of accidents or failures.
Maintenance inspections matter for every facility because they are essential for saving costs, ensuring reliability, promoting safety, complying with regulations, boosting efficiency, extending asset life, maintaining productivity, and upholding overall quality.
Steps to Implement an Effective Preventive Maintenance Inspection Plan
Implementing a successful preventive maintenance inspection plan requires careful planning and execution. Here are some crucial steps to follow:
Identify critical assets for operational continuity
Begin by identifying the key assets that require preventive maintenance inspections. This could include machinery, equipment, buildings, or any other infrastructure that plays a vital role in your operations.
When identifying critical assets, it is important to consider their importance to the overall functioning of your organization.
Here are some considerations that can be useful:
- How crucial is the asset to the day-to-day functioning of our operations?
- Does the asset play a vital role in supporting or interacting with other systems?
- Are there safety considerations associated with the asset's functionality or failure?
- Are there regulatory requirements specifying maintenance for certain assets?
- What is the maintenance history and performance track record of the asset?
- What would be the financial consequences if the asset fails unexpectedly?
- Where does the asset stand in terms of its lifecycle, and does its age impact its reliability?
- Does the asset align with your strategic goals or long-term plans?
Create a comprehensive checklist for maintenance tasks
Developing a checklist or protocol is a pivotal step in the process of implementing preventive maintenance schedule for critical assets. This checklist should delineate the specific inspections to be carried out for each asset, covering all pertinent aspects, such as electrical systems, mechanical components, safety features, and more. Creating a comprehensive checklist is essential to ensure that no important facet of the asset is overlooked during inspections.
For example, if you are inspecting a production machine, your checklist may include items such as:
✅ Checking for abnormal vibrations.
✅️ Inspecting lubrication levels.
✅ Examining the condition of belts and bearings.
The checklist acts as a structured guide for maintenance personnel, systematically directing them through the inspection process.
It ensures that every critical element of the asset is examined, promoting consistency and reliability in the maintenance routine – leaving no room for oversight.
Define inspection frequencies for every asset class
Determining the appropriate inspection frequencies for each asset in preventive maintenance involves considering factors like manufacturer recommendations, industry standards, and historical data.
To establish an optimal schedule, consider the following:
💡 Manufacturer recommendations:What are the manufacturer's suggested inspection intervals for critical components?
Example, for a diesel generator, if the manufacturer recommends checking fuel filters every 200 operating hours, incorporating this guideline ensures timely inspections aligned with the equipment's specifications.
💡 Industry standards: Are there industry regulations specifying inspection frequencies for similar assets?
For instance, in the healthcare sector, where regulatory standards dictate equipment safety, following guidelines that prescribe monthly inspections for medical imaging devices ensures compliance with industry regulations.
💡 Historical Data on Asset Performance: What patterns or trends emerge from historical data regarding asset failures or wear?
💡 Usage Patterns: How frequently is the asset used, and what is the intensity of its usage?
Example, For a conveyor system in a busy distribution center, where high throughput is constant, more frequent inspections, perhaps bi-weekly, may be necessary to manage wear from heavy usage.
Train inspection teams
Provide thorough training to the individuals responsible for conducting the inspections. They should be knowledgeable about the equipment being assessed as well as the inspection techniques and protocols.
The training should cover not only the technical aspects of the assets being inspected but also the proper use of inspection tools and equipment.
Document findings and actions
Maintain detailed records of all inspections, including identified issues, recommended actions, and completed repairs. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future inspections and helps track the overall performance of assets.
These records can help identify recurring issues, track the effectiveness of preventive maintenance measures, and provide valuable insights for future inspections.
But documentation is not a cakewalk. It means you'll have to get lost in the spreadsheet maze forever without proper direction. That's when a robust and comprehensive CMMS like Facilio comes to play.
Facilio, a leading maintenance management platform, can significantly streamline the documentation process and enhance the efficiency of managing inspections, issues, and repairs.
Here's how:
Facilio provides a centralized platform to store all inspection records, identified issues, recommended actions, and completed repairs, eliminating the need for scattered spreadsheets.
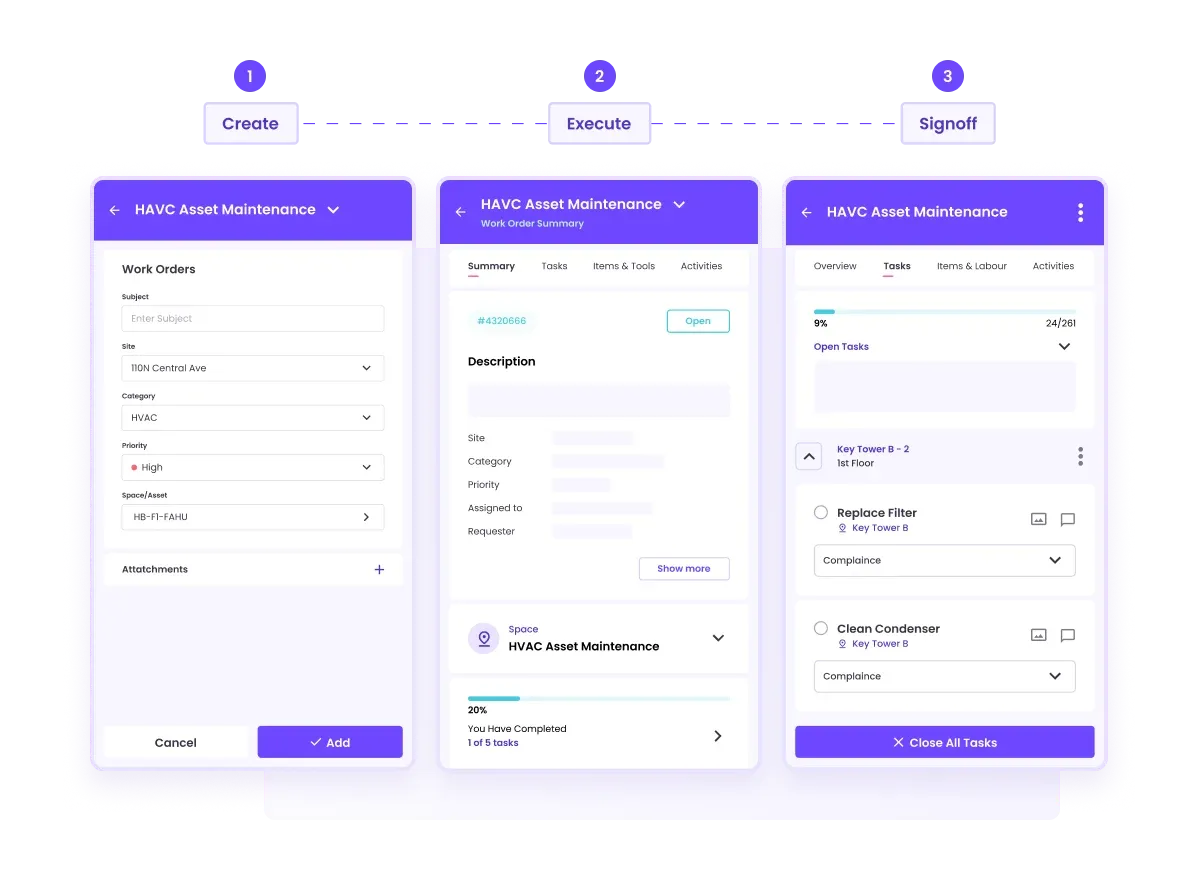
Its intuitive interface simplifies the documentation process. It allows users to easily input data, update records, and retrieve information without complexity.
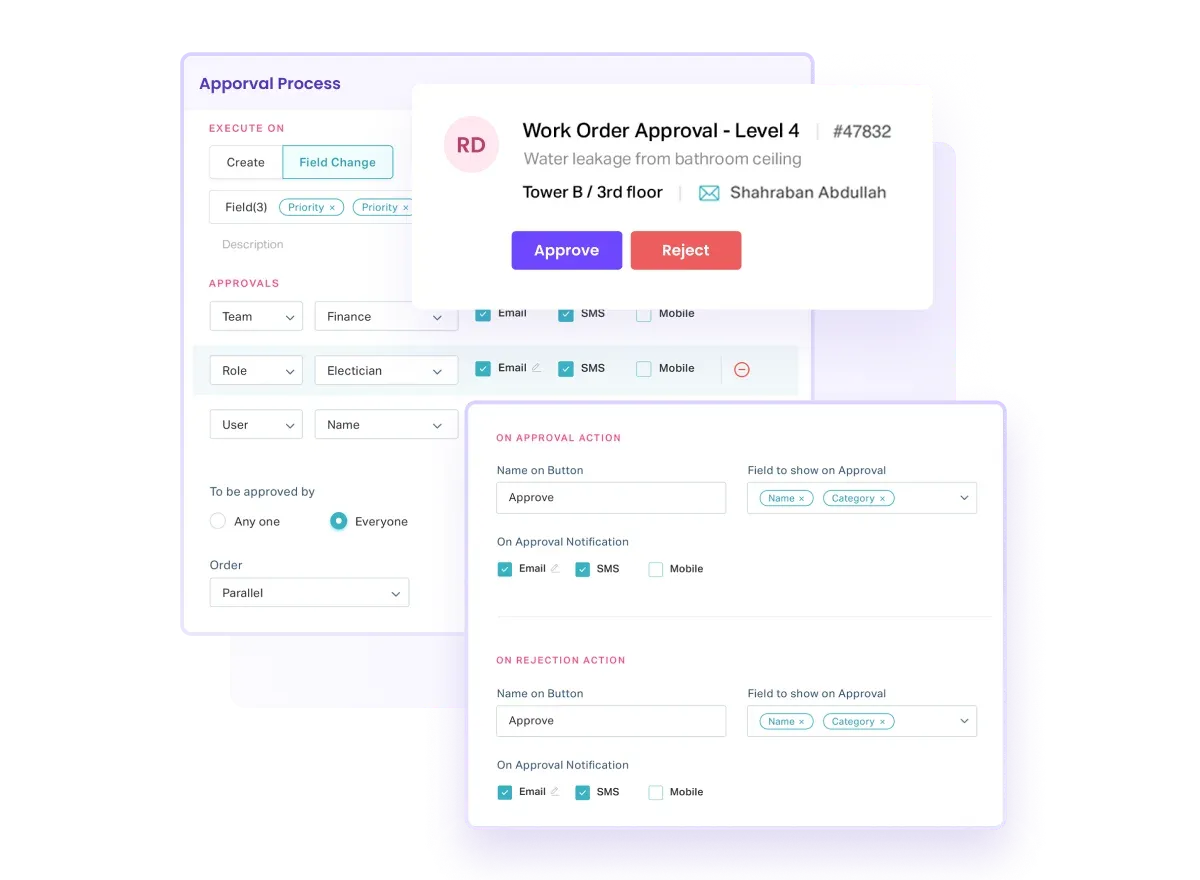
You can also automate workflows with existing templates or custom ones, streamlining the process from issue identification to resolution, reducing manual intervention, and accelerating the completion of repairs.
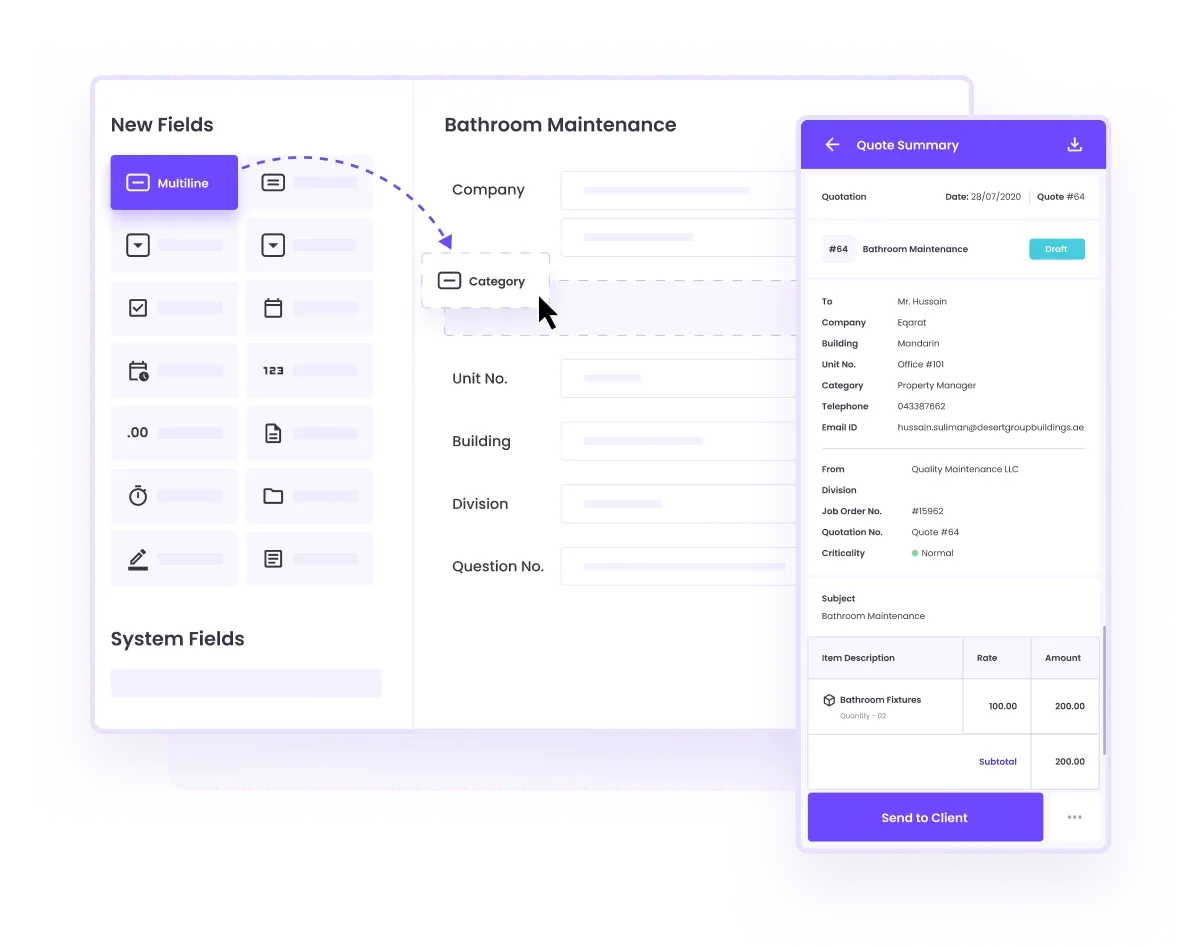
Interested in learning what a platform would bring to your business?
That's easy. This Connected CMMS RoI calculator generates a custom report on how much you could save by switching to a platform in seconds.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement
Continuous improvement is essential for the success of your preventive maintenance inspection plan. Regularly review and refine the plan based on feedback, data analysis, and emerging best practices to optimize processes and enhance efficiency.
Incorporate feedback from inspection teams, analyze asset performance data, and stay updated on industry best practices to identify and implement improvements.
This iterative approach will optimize processes and yield better results over time. Implement an effective preventive maintenance inspection plan to minimize breakdowns, maximize asset performance, and save time and money, ensuring the long-term success of your operations.
Types of Preventive Maintenance Inspections
There are several types of preventive maintenance inspections, each tailored to the specific needs of different industries and equipment.
Let's explore some of the most common ones:
Time-based inspections:
- Performed on a predefined schedule (monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Ideal for equipment requiring routine maintenance to prevent wear and tear.
- Example: Aviation industry conducts regular time-based inspections on aircraft components like engines and landing gear to ensure optimal condition and reduce the risk of unexpected failures during flights.
Condition-based inspections:
- Triggered by specific indicators (hours of operation, decrease in performance, data points).
- Common in industries where equipment performance directly impacts production output.
- Example: Manufacturing plants use sensors to monitor parameters like temperature and vibration, initiating inspections when anomalies are detected to minimize downtime and maintain product quality.
Predictive inspections:
- Utilize advanced technologies like sensors and data analytics to analyze real-time data.
- Predict when maintenance is required by monitoring factors like vibration, temperature, or fluid levels.
- Common in industries with severe consequences for unexpected failures.
- Example: Oil and gas sector employs predictive inspections in pipelines and refineries to identify potential failures in advance, preventing accidents, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Prescriptive inspections:
- Goes beyond predicting maintenance needs and recommends specific actions to be taken.
- Optimize decision-making in complex systems with multiple interacting components.
- Example: Healthcare industry uses prescriptive inspections for medical devices, providing detailed recommendations for maintenance tasks like calibrations or part replacements based on real-time data analysis. This streamlines maintenance operations, reduces downtime, and enhances patient care quality.
Use Facilio to Plan Your Preventive Maintenance Inspections
Any inspection plan comes down to effective execution and management. You need to implement a reliable system that ensures seamless planning, execution, and monitoring of preventive maintenance inspections.
Facilio's Connected CMMS platform streamlines the entire process, ensuring optimal planning, execution, and management of preventive maintenance inspections.
Curious? You can see Facilio in action for free here.



